Lawn mowers can be more difficult to start in cold weather. If you use your lawn mower to move snow or are using it on those cool mornings and evenings in the spring and fall you may be running into this problem. There are several items that can affect starting a mower in cold weather.
I have put together a list of items that can result in a mower not starting in cold weather along with items that can prevent a mower from starting in general. These are problems that may have popped up on a cold day, but not necessarily due to cold weather.
A lawn mower may be hard to start in cold weather when the choke is not closed to start a cold engine; the wrong oil viscosity is used; the battery is bad or not charging; the fuel tank is empty or contains old fuel; the air filter is plugged; the fuel system is clogged; the carburetor is dirty; a switch is bad; the spark plug is bad, or the starter solenoid is not working.
Follow all safety precautions listed in your operator’s manual before attempting to troubleshoot and repair your lawn mower.

This post may include affiliate links. Purchases made through these links may provide a commission for us, at no extra cost to you. As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.
Follow all safety instructions provided in your equipment operator’s manual before diagnosing, repairing, or operating. Consult a professional if you don’t have the skills, or knowledge or are not in the condition to perform the repair safely.
15 Reasons a Lawn Mower Won’t Start When Cold
Faulty Choke or Incorrect Setting
The function of the choke is to restrict airflow to the carburetor allowing a higher concentration of fuel to be pushed into the combustion chamber of the cylinder. This is needed to start a cold engine.
The choke linkage may be stuck and the choke cable may be out of adjustment causing the choke to not properly open and close. This can cause a lawn mower not to start when cold.
Solution: Remove the air filter housing and locate the choke valve. Move the choke lever to ensure it is opening and closing correctly. Adjust the cable and lubricate the choke linkage as needed so the choke is closed when the choke lever is engaged and open when it is not.
Wrong Oil Viscosity
The engine oil viscosity is important to keep the engine properly lubricated. Using an oil that is too thick will not allow the internal engine parts to move freely. This can cause engine problems that may affect the starting of your lawn mower.
The ambient temperature you are operating your mower in can affect the oil viscosity you must use.
Most lawn mower manufacturers recommend using a SAE30 or 10W-30 engine oil, but you may have to change your oil viscosity to a 5W-30 when operating in colder temperatures especially when you use a riding mower for snow maintenance during the winter.
Check out this chart provided by Kawasaki Motors that reflects the oil viscosity in relation to temperatures:
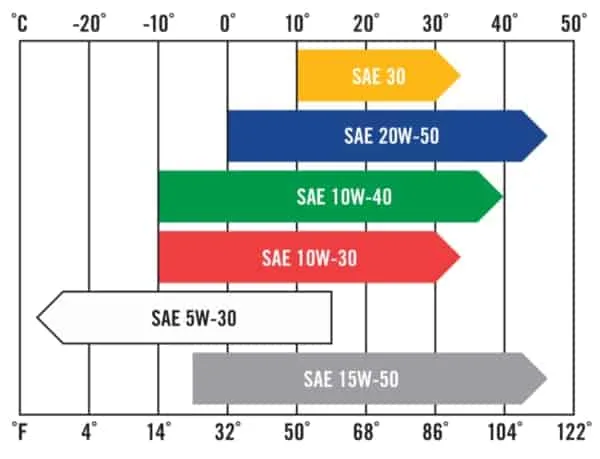
Solution: Refer to your operator’s manual for the oil viscosity recommended. If you are running the incorrect oil, drain the engine oil and refill with the correct oil to meet your outdoor temperature needs.
Bad Battery or Loose Terminals
All lawn mowers, other than manual start push mowers using recoils, require a battery to start. The cables and terminals can come loose and no longer make a good connection. The terminals may also begin to corrode affecting the connection.
A battery can fail over time or freeze and no longer hold a charge when left in cold temperatures without a good charge. If ambient temperatures fall under 20 degrees and you don’t have at least a 20% charge in your battery, your battery may freeze.
As the temperature decreases, you must have a greater charge in your battery to ensure it doesn’t freeze and go bad as shown in this table:
| Battery Charge | 12-Volt Battery | 6-Volt Battery | Battery Freezing Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40% | 11.97 V | 5.98 V | 20 degrees Fahrenheit |
| 20% | 11.67 V | 5.84 V | 5 degrees Fahrenheit |
| Zero Charge | — | — | 20 degrees fahrenheit |
Solution: Make sure your cables and battery terminals are secure. Clean any corrosion you find on your terminals using a baking soda solution (2 cups water to 3 heaping tablespoons of baking soda) and a wire brush. Once you confirm you have a good connection, continue testing the battery.
Test your battery with a multimeter. You want a reading at about 12.7 volts. Charge your battery if it is lower than this level. You can find more information on charging your battery here. A battery that is dead or won’t hold a charge must be replaced.
To find more information on caring for your battery during the winter season, check out this guide so you can make sure your battery is in good condition for the next mowing season, “Winter Lawn Mower Battery Care“.
Bad or Old Fuel
Old gas sitting in a lawn mower can cause fuel restrictions and wear the fuel components. Most types of gasoline contain ethanol, a corn-based fuel. This product may be friendly to the environment, however, it is not friendly to the small engine in your lawn mower.
The sticky substance left behind when ethanol, and the moisture it attracts, evaporates can keep fuel from running through the mower.
Because gasoline begins breaking down as quickly as 30 days after you purchase it, it’s important to consume the fuel within this timeframe or stabilize it so it lasts longer.
Solution: Remove the old fuel using a fuel siphon. Add fresh fuel with a fuel additive to clean your fuel system, reduce moisture and stabilize it. I have had good results using a product called Sea Foam Motor Treatment. You can read more about why I use Sea Foam here.
Bad Spark Plug or Loose Connection
A dirty spark plug or an incorrectly gapped spark plug can prevent your mower from starting when it is cold. The spark plug can develop carbon buildup that will cause spark problems.
This buildup can be cleaned with a wire brush. I prefer to replace the spark plugs because they are inexpensive and necessary to keep the mower running at its best.
Solution: Remove your spark plug and inspect it for signs of carbon buildup, a cracked porcelain insulator, or a burnt electrode. Replace with a new spark plug(s).
Make sure to gap them according to manufacturer specifications and that the spark plug wires are securely attached. You can find this information in your operator’s manual.
Plugged Air Filter
A lawn mower requires clean air to run. The air filter prevents dirt and debris from entering the air intake and contaminating the engine. Dirt in the engine can cause significant engine damage including scoring of the cylinder and gasket failures.
Never run your mower without an air filter even if it’s only for a short period of time while you source a new filter.
When an air filter gets plugged in so air is no longer able to pass through the filter, your mower won’t start. It is important to regularly check the air filter and keep it clean.
By checking, cleaning, and replacing this inexpensive part when needed, you can prevent an expensive engine repair.
Solution: Carefully remove the air filter from the air filter housing so you don’t allow dirt to fall into the air intake. If you find dirt in the housing, wipe it out with a clean cloth. Follow one of the following procedures for your type of air filter:
Clean a paper air filter
- Knock out the excess dirt in the filter by tapping it against a solid surface.
- Hold the filter up to a light source and check for light shining through the paper element.
- Reuse the filter if you can see light pass through the paper. If you cannot, replace your filter with a new air filter.
- Install the air filter and attach the cover.
Clean a foam air filter
- Determine whether you can reuse your filter before cleaning it. If your filter has dark spots or is dry and brittle, replace the filter with a new one.
- If your filter is in good condition, proceed with washing it with mild dish soap and water to remove dirt from the filter.
- Rinse the filter and lay it flat to dry. Placing it outdoors in the sun will speed up the process.
- Once the filter is dry or if you are using a new foam filter, add clean engine oil to lightly saturate the filter. You don’t want it dripping with oil.
- Install the filter into the housing and attach the cover.
Plugged Fuel Filter
The fuel filter keeps dirt from entering the fuel system. The fuel filter on a lawn mower is typically an inline filter installed between the fuel lines after the fuel leaves the fuel tank and before it reached any fuel components.
When the fuel is extremely dirty or you don’t change your fuel filter annually, you can develop a buildup of dirt in the filter that no longer allows fuel to pass through the filter. This can be the reason your lawn mower won’t start when cold.
Solution: Replace a plugged fuel filter. You will find a small arrow on the side of the filter. The filter must be installed with the arrow pointed in the direction of your fuel flow.
Blocked Fuel Line
A lawn mower fuel line can become clogged by dirt and the sticky substance left behind by old gasoline. This keeps fuel from getting to your carburetor and to your engine. Read more about identifying a clogged fuel line here.
Solution: Remove the fuel line, spray carburetor cleaner into the tube, and use compressed air to blow air through the tube until the line is free of dirt and gummy residue. Repeat as necessary. Replace the fuel line with a new line when you can’t remove the clog.
Faulty Fuel Pump
A mower uses a fuel pump when the carburetor is placed higher than the fuel tank. The fuel pump is needed to pump fuel from the fuel tank up to the carburetor. The pump can fail over time from old fuel sitting in the pump and deteriorating the pump components.
Solution: To identify a failing fuel pump, first, inspect your vacuum fuel pump for cracks. If you see fuel outside of the fuel pump or cracks in the pump, the pump will no longer be able to create the pressure needed to pump fuel.
Using the fuel shut-off valve, if your mower has a valve, or pinch pliers to stop and start fuel flow will help you control fuel flow. Stop and start flow to make sure you are getting fuel to the pump.
Once you verify your pump is getting fuel, check to make sure that fuel is being pumped out of the pump in a steady or pulsating flow by removing the fuel line from your carburetor and placing it in a container.
Start your mower. The fuel pump is working correctly if a steady or pulsating flow of fuel is coming out of the fuel line. Replace a bad fuel pump.
Dirty Carburetor
Your mower uses a carburetor to regulate the amount of gas mixed with air allowed into the cylinder to form combustion.
The additives added to fuel, including ethanol, can cause gummy substances to form in your carburetor. The substance clogs the small parts in your carburetor restricting fuel.
Solution: If you are somewhat mechanical, you can try to clean the carburetor on your lawn mower. If you are not, have a local lawn mower repair shop perform the work. You can find steps for cleaning your carburetor in this article.
You may choose to replace the carburetor if it appears to be in very bad condition. Have a small engine repair shop clean the carburetor if you don’t want to attempt the cleaning or rebuilding the carburetor.
Bad Starter Solenoid
A lawn mower solenoid on your lawn mower is an electromagnetic switch like an on-off switch that actuates the starter motor to turn over the engine.
A click or hum when turning your ignition key is an indication to check your solenoid. Another indication your lawn mower solenoid may be bad is when a wire attached to your solenoid gets hot and begins to smoke or melt.
Solution: Test your lawn mower solenoid by following the steps here. Replace your solenoid if it is found to be bad.
Bad Safety Switch
Your lawn mower may use several safety switches in its operator’s presence control system. The switches are designed to kill the engine when the operator leaves the seat and the mower deck is engaged.
A faulty switch may not recognize when the operator is in or out of the seat causing your mower not to start.
Refer to your operator’s manual for the different types of safety switches used in your type of lawn mower.
Solution: You can temporarily bypass the safety switch to identify a bad switch. Do not operate a mower without the safety switch installed for your safety. Always have safety switches installed and working on your equipment. Replace a bad switch.
Faulty Charging System
While the charging system isn’t the main reason your lawn mower won’t start, it does affect the battery which can prevent your mower from starting when cold.
A faulty charging system on your lawn mower will drain the battery and not keep it charged causing your mower not to start.
If you find the battery keeps draining and you have to continually charge it each time you go to use your mower, you may have a problem with the charging system.
A bad stator, alternator, or several other electrical parts can be the cause of your charging system problem. Read this article to test your charging system here using an ohmmeter.
Solution: I recommend having your lawn mower looked at by a professional lawn mower dealership to identify your charging system. There are so many pricey electrical components that can cause your starting problem.
If you are not experienced with the charging system, you will probably just be throwing parts at your mower hoping it will solve the problem. This can get very expensive especially when most stores do not allow you to return electrical components if they aren’t the cause of your problem.
Still Having Problems with Your Lawn Mower?
Lawn mower ownership doesn’t come without its frustrations. Own a mower long enough, you are bound to run into many lawn mower problems including starting, smoking, leaking, cutting, and overheating.
For mower troubleshooting, check out my guide Common Lawn Mower Problems: Solved.
